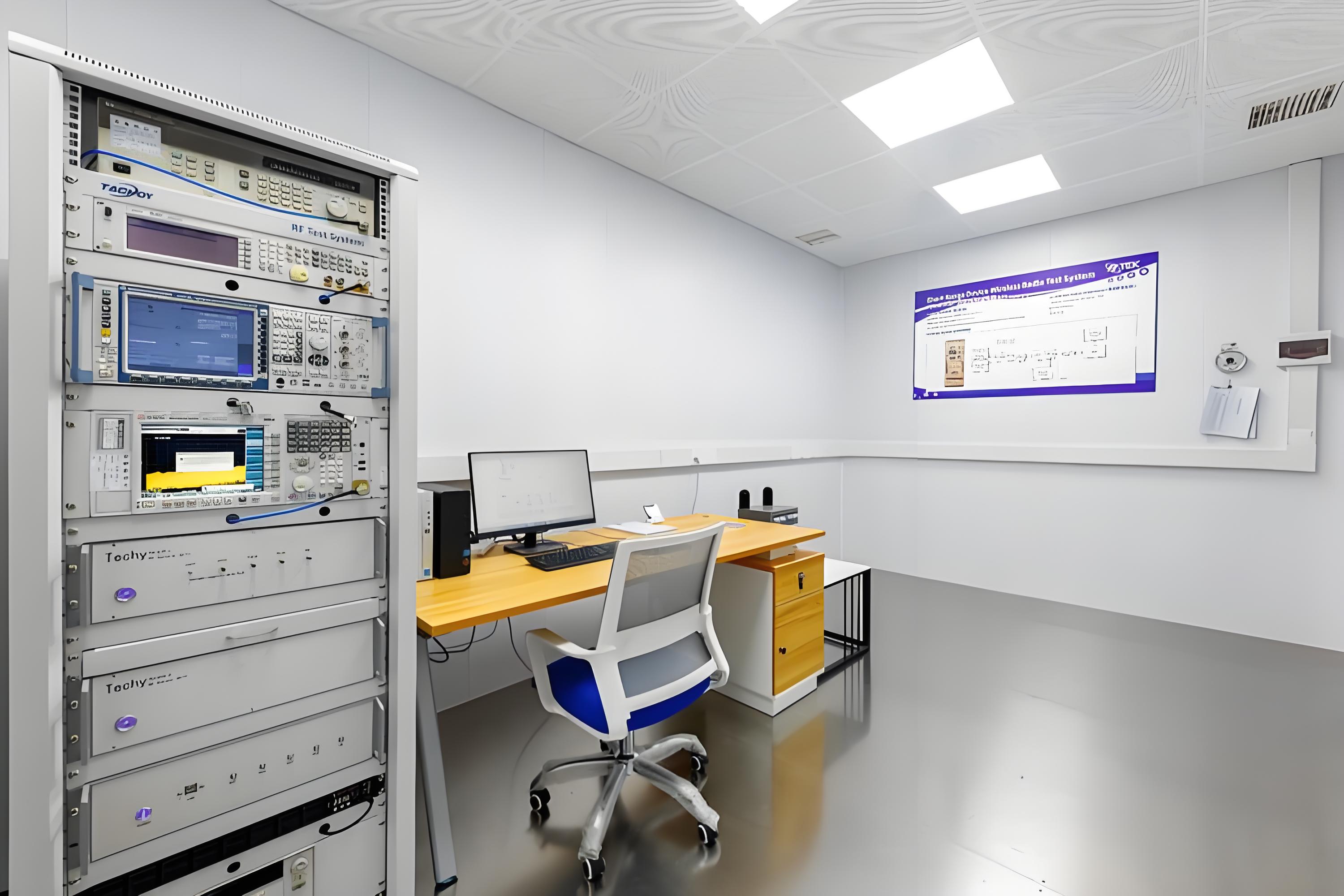
Before being released to the market, electronic products must undergo a series of tests and certifications to ensure their functionality, safety, and compliance with market regulations. Below are the main aspects of testing and certification projects for electronic products:
1. Functional Testing
- Purpose: Verify whether the product operates as designed.
- Content:
- Hardware Function Testing: Check whether modules (e.g., power supply, communication interfaces, sensors) work properly.
- Software Function Testing: Test whether the firmware or embedded software functions and logic are correct.
- Compatibility Testing: Ensure the product is compatible with other devices or systems.
2. Performance Testing
- Purpose: Assess the product’s performance under various conditions.
- Content:
- Temperature and Humidity Testing: Evaluate the product’s performance in high-temperature, low-temperature, and high-humidity environments.
- Aging Testing: Run the product continuously for extended periods to evaluate its durability and stability.
- Power Consumption Testing: Measure the product’s power consumption to ensure it meets design specifications.
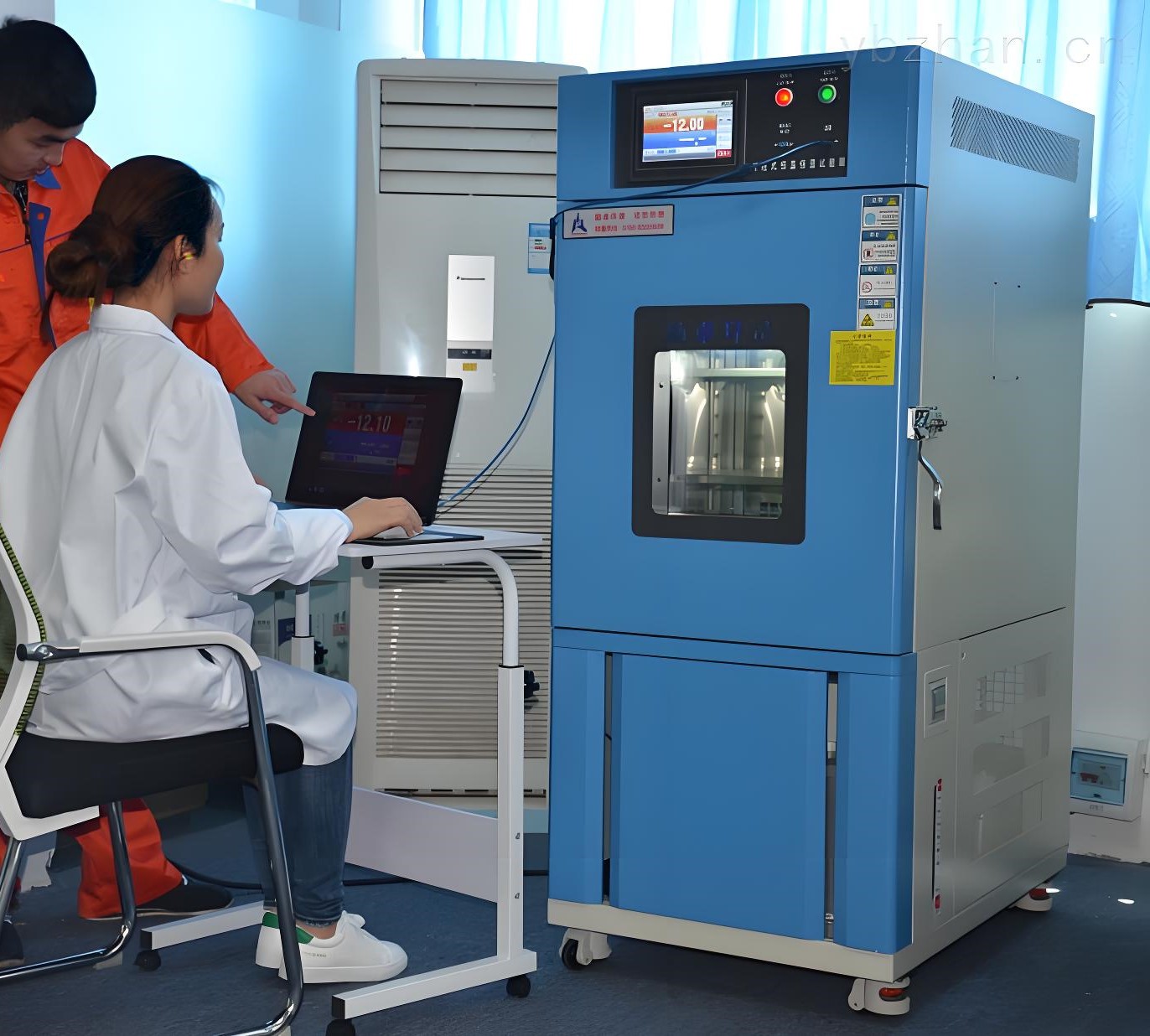

3. Electrical Safety Testing
- Purpose: Ensure the product’s electrical safety to protect users and equipment.
- Content:
- Dielectric Withstand Test: Check the product’s insulation capability under high voltage.
- Grounding Resistance Test: Ensure the grounding resistance meets requirements.
- Leakage Current Test: Detect unsafe leakage currents in the product.
4. Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Testing
- Purpose: Ensure the product operates normally in an electromagnetic environment without interfering with other devices.
- Content:
- Radiated Emission Test: Measure the electromagnetic waves emitted by the product to ensure they do not exceed standard limits.
- Conducted Emission Test: Detect electromagnetic interference conducted through power lines.
- Immunity Test: Evaluate the product’s resistance to external electromagnetic interference (e.g., ESD, EFT).
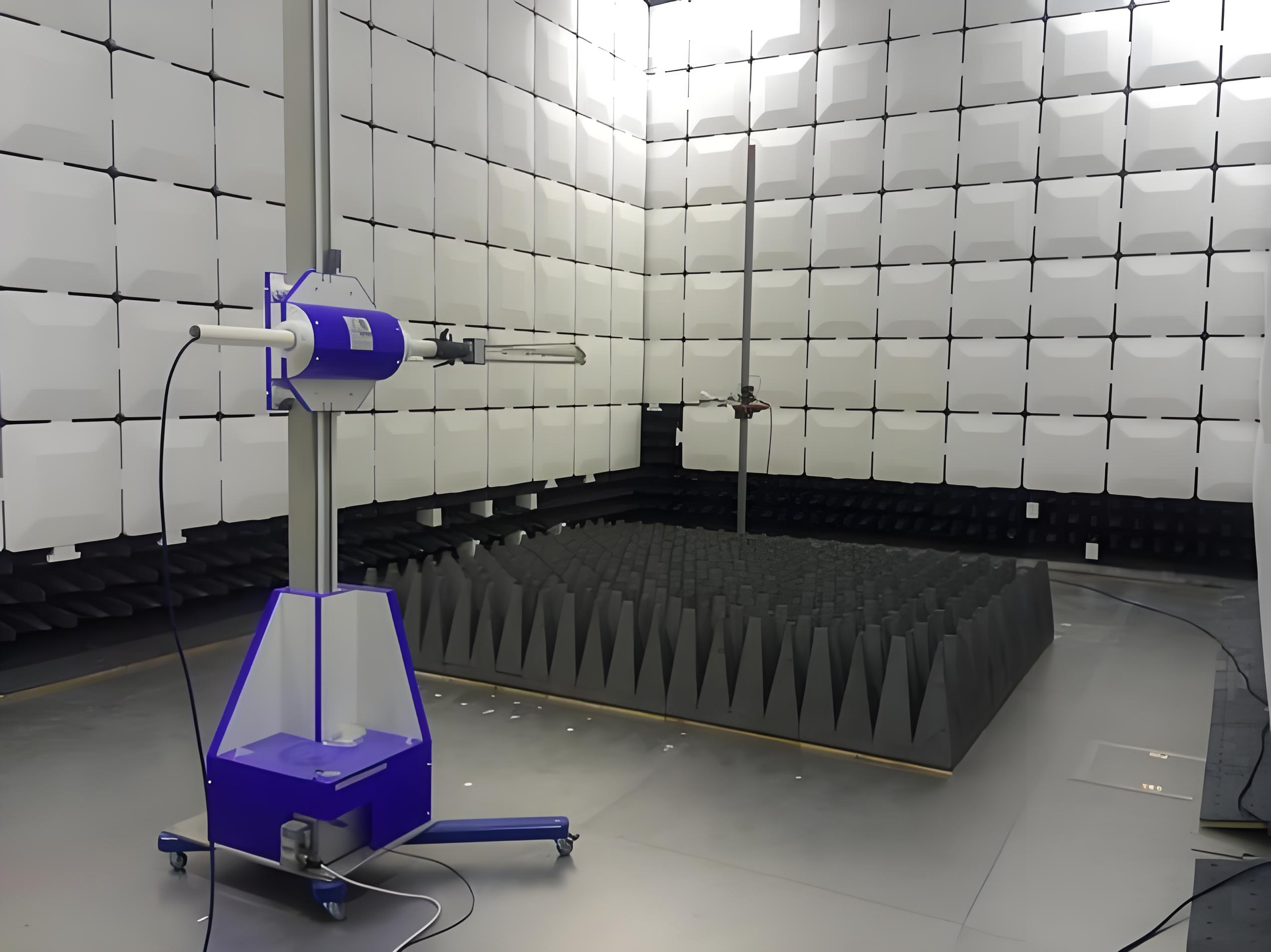
5. Wireless Communication Testing (for wireless devices)
- Purpose: Ensure wireless devices’ communication performance and spectrum compliance.
- Content:
- Transmit Power Test: Check whether the transmission power of the wireless signal meets standards.
- Spectrum Analysis: Ensure the signal frequency complies with regulatory requirements.
- Sensitivity Test: Assess the device’s ability to receive weak signals.
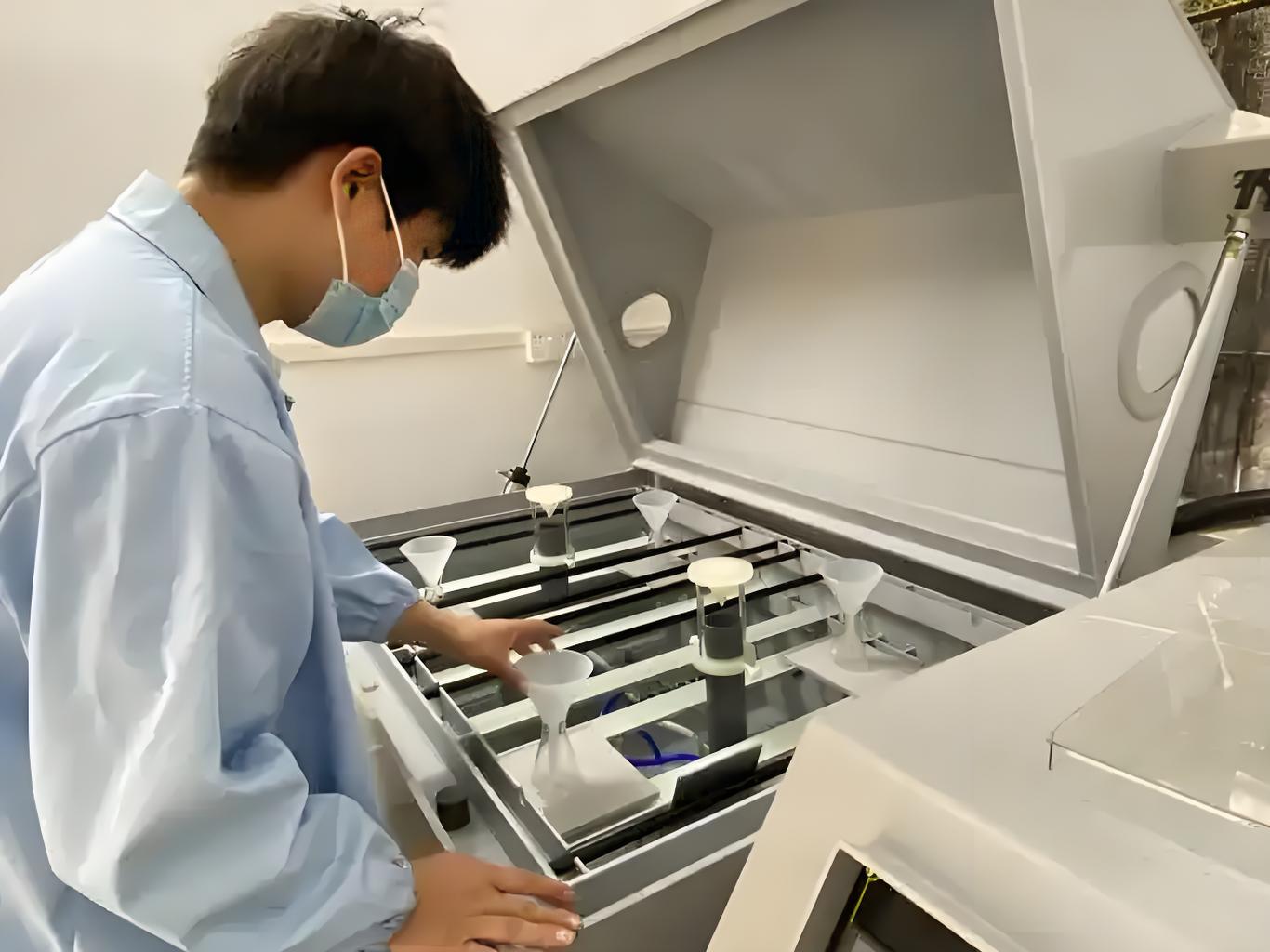
6. Environmental Reliability Testing
- Purpose: Verify the product’s reliability under various extreme environmental conditions.
- Content:
- Vibration Test: Simulate vibration conditions during transportation or usage.
- Drop Test: Assess the product’s performance after being dropped from a certain height.
- Salt Spray Test: Evaluate the product’s durability in a corrosive environment.

7. Certification Projects
- Mandatory Certifications:
- CCC Certification (China): Mandatory safety certification for products in the Chinese market.
- CE Certification (EU): Indicates compliance with EU safety and environmental standards.
- FCC Certification (USA): Ensures electromagnetic compatibility and radio frequency compliance for the U.S. market.
- Industry-Specific Certifications:
- UL Certification (North America): Safety certification for electrical products.
- RoHS Certification (Global): Restriction of Hazardous Substances directive to ensure the product is free of harmful chemicals.
- ISO Standards: For example, ISO 9001 (Quality Management System Certification).


