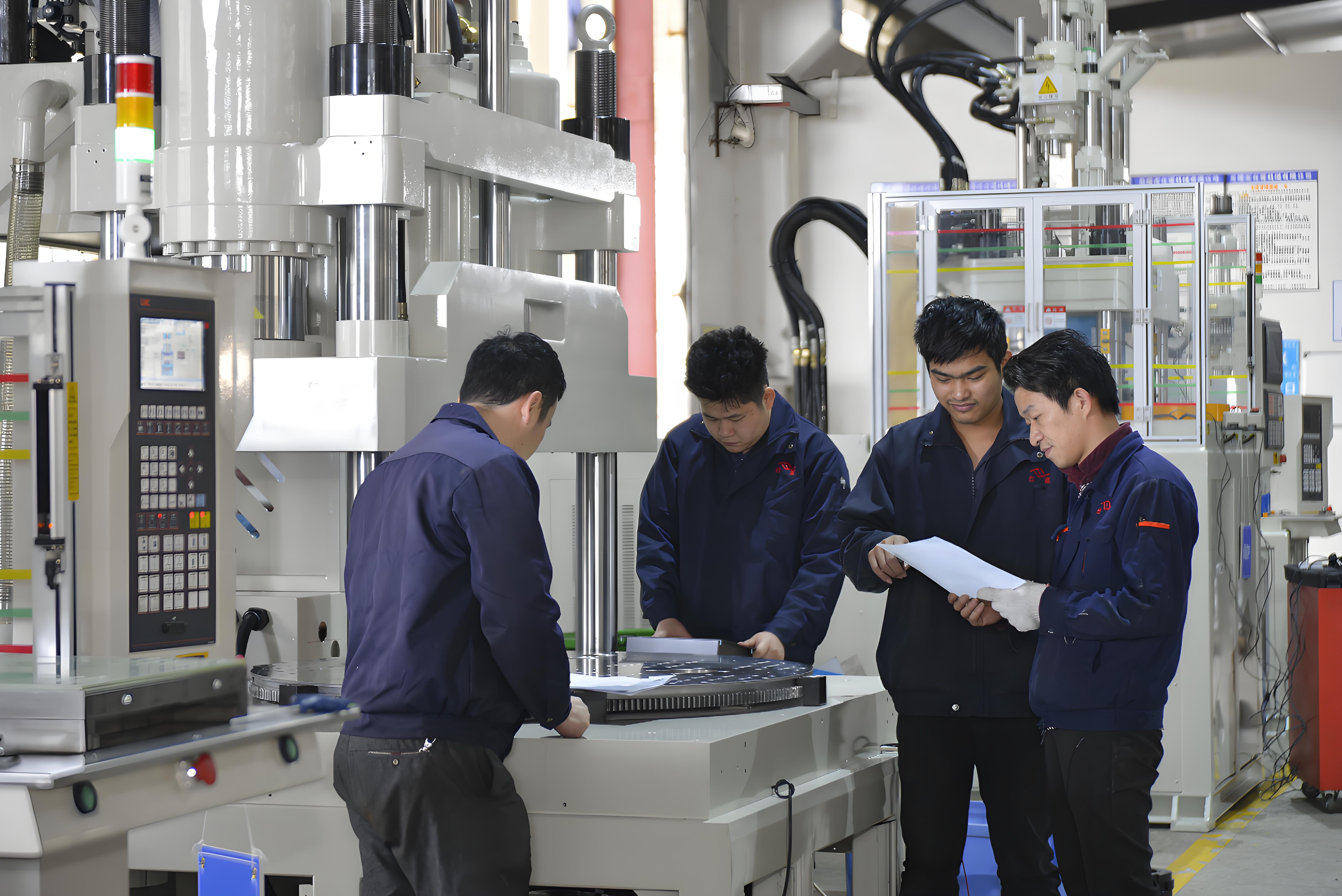
The design of a product’s appearance and enclosure must meet functional requirements while considering aesthetics, structural integrity, and production cost. After design completion, a series of validation processes are necessary to ensure feasibility and reliability. Below are the main steps for designing and validating product appearance and enclosures:
1. Requirement Analysis
- Define the goals for appearance design, including product functionality, style, size constraints, and material selection.
- Determine environmental adaptability requirements (e.g., waterproof, dustproof, drop resistance) and user experience needs (e.g., ergonomic design).
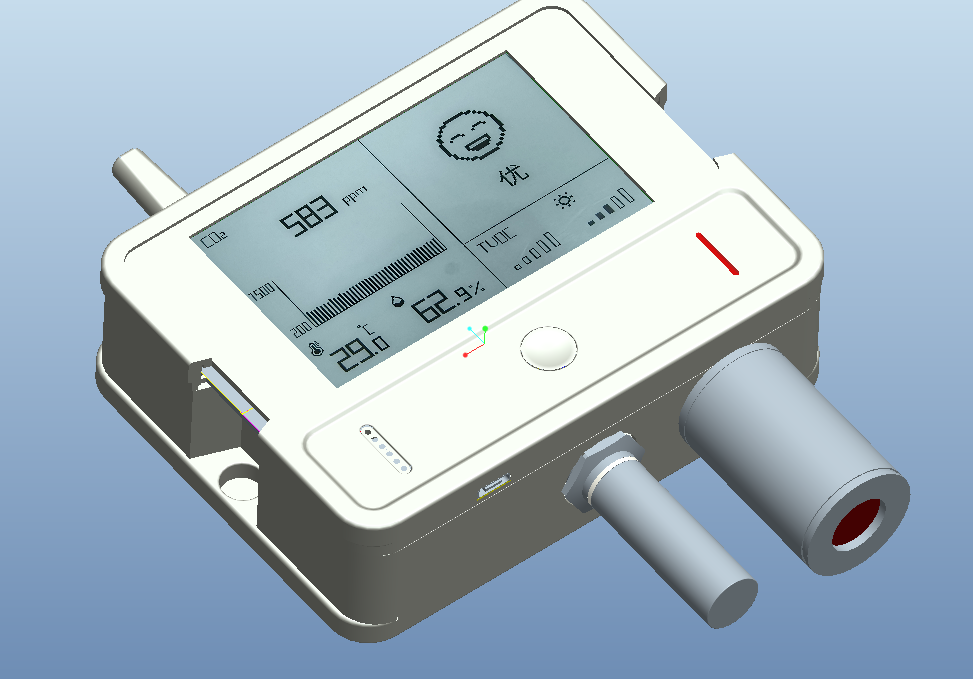
2. Appearance Design
- Concept Design: Create initial sketches or concepts using design tools (e.g., Photoshop, Sketch).
- 3D Modeling: Use 3D modeling software (e.g., SolidWorks, Pro/E, Fusion 360) to turn design concepts into three-dimensional models.
- Design Review: Conduct team discussions to evaluate the feasibility of the model and ensure it aligns with brand style and functional requirements.
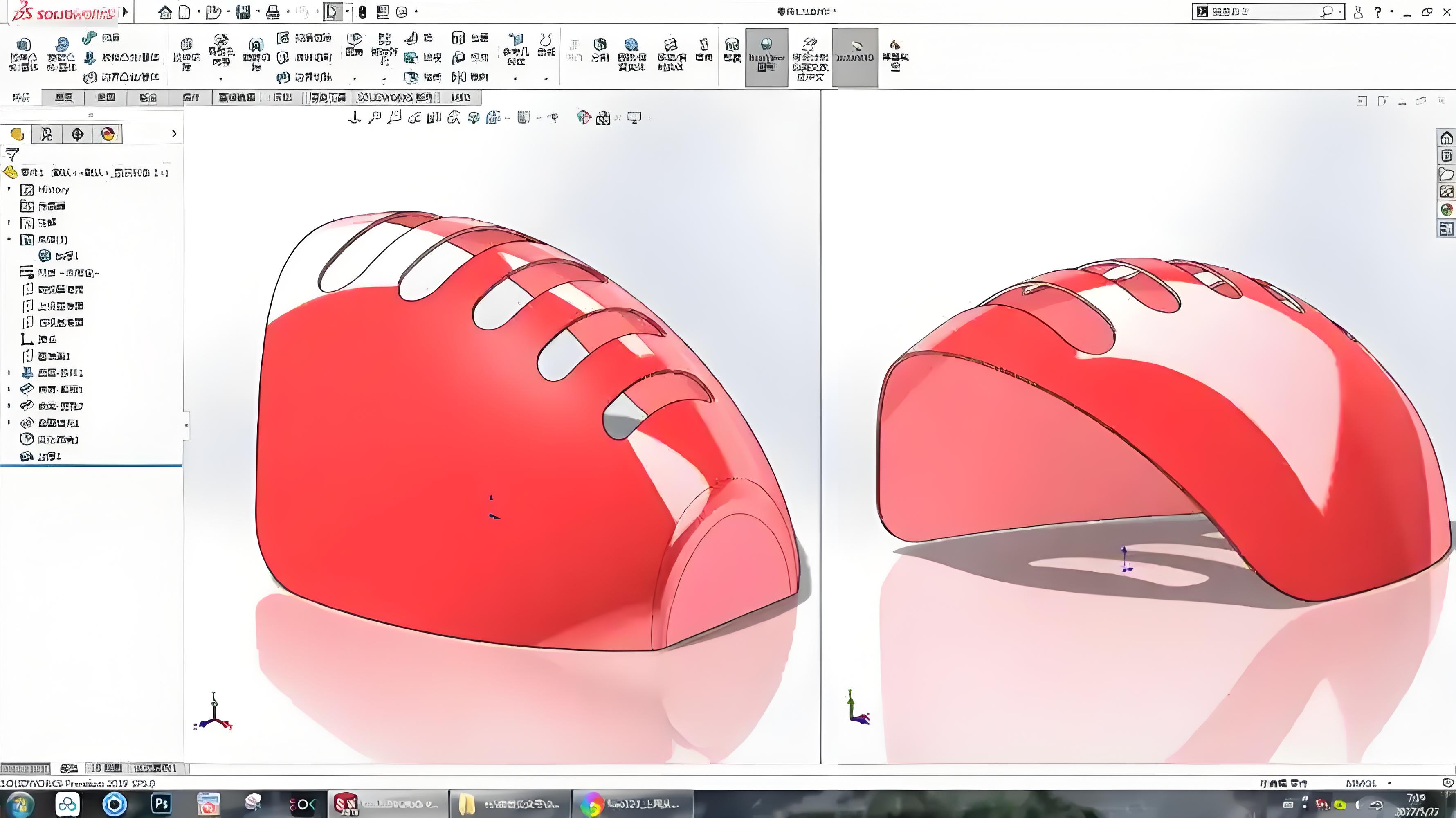
3. Enclosure Structural Design
- Internal Layout Planning: Design internal supports and fixtures based on the layout of circuit boards, components, and batteries.
- Material Selection: Choose suitable materials (e.g., plastic, metal, or composites) based on cost, strength, and manufacturing process.
- Process Design: Determine the production method (e.g., injection molding, stamping, or 3D printing) and surface finishing (e.g., texture, painting).
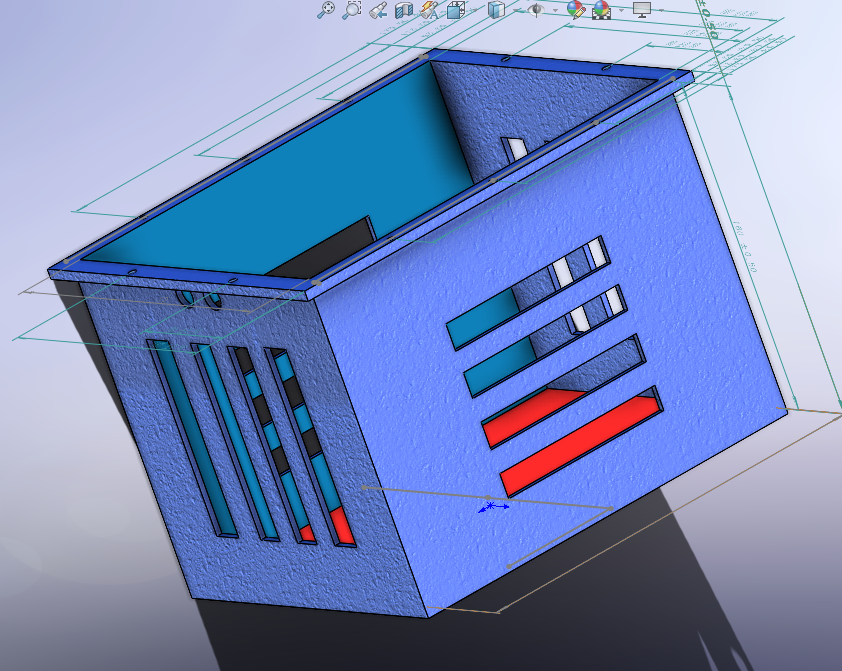
4. Prototype Creation
- Rapid Prototyping: Use 3D printing or CNC machining to create samples for preliminary verification of the appearance and structure.
- Assembly Testing: Verify whether the enclosure fits with internal components and adjust unreasonable designs.

5. Validation and Testing
- Function Validation: Ensure the enclosure supports product functionalities (e.g., heat dissipation, antenna signal transmission).
- Reliability Testing:
- Waterproof Testing: Verify if the enclosure meets waterproof ratings (e.g., IP67).
- Impact and Drop Testing: Assess the enclosure’s resistance to drops.
- Temperature and Humidity Testing: Check material stability in extreme environments.
- User Experience Testing: Gather user feedback to optimize the design for usability and ergonomics.
6. Production Preparation
- Mold Design: Develop molds based on the final design to ensure product consistency in mass production.
- Trial Production: Conduct small-scale trial production to validate the feasibility of molds and manufacturing processes.
- Refinement and Optimization: Further optimize the design and process based on issues identified during trial production.
7. Mass Production and Monitoring
- Mass Production Launch: Begin large-scale manufacturing of the enclosures.
- Quality Monitoring: Regularly inspect the quality of enclosures during production to ensure they meet design specifications.
- Continuous Improvement: Optimize enclosure design and processes based on market feedback.


